SQL Limit
What is the LIMIT statement in SQL?
The LIMIT clause in SQL is used to specify the maximum number of rows returned by a SELECT statement. It is used to limit the number of rows retrieved from a database.
Specifying the maximum number of rows to be returned in a query result helps to reduce the amount of data transmitted from the database to the application, making the query more efficient and reducing the memory footprint.
SQL LIMIT helps with:
- Resource utilization: Save system resources by avoiding processing unnecessary data, improving data platform efficiency and reducing cost.
- Security and privacy: Enforce security and privacy policies by limiting data access to only what is necessary.
- Usability: Limiting the results can make it easier to handle and analyze data within an application; plus, the results are returned faster.
Here’s the basic SQL Limit syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
LIMIT number_of_rows;- number_of_rows represents the maximum number of rows to be returned in the result set.
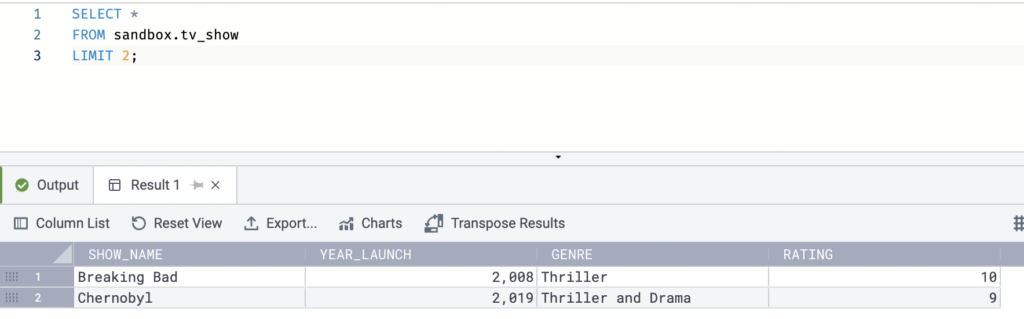
For example, the following SQL Limit statement returns 2 rows from the tv_show table.
SELECT *
FROM sandbox.tv_show
LIMIT 2;